-
TIL*2 - 05.17,9TIL 2024. 5. 20. 00:47
전처리에 시간이 많이 든다
= 이거 파고 들려면 어디까지 들어가야 할지 모르겠다.
dtype('O') : Object
더보기'b' boolean
'i' (signed) integer
'u' unsigned integer
'f' floating-point
'c' complex-floating point
'O' (Python) objects
'S', 'a' (byte-)string
'U' Unicode
'V' raw data (void)DataFrame <-> List
더보기to.DF
L = ['Thanks You', 'Its fine no problem', 'Are you sure'] #create new df df = pd.DataFrame({'col':L}) #defalut column name = '0' print (df) col 0 Thanks You 1 Its fine no problem 2 Are you suredf = pd.DataFrame({'oldcol':[1,2,3]}) #add column to existing df df['col'] = L print (df) oldcol col 0 1 Thanks You 1 2 Its fine no problem 2 3 Are you sureDF to list
.tolist()
import pandas as pd # Creating a dictionary to store data data = {'Name':['Tony', 'Steve', 'Bruce', 'Peter' ] , 'Age': [35, 70, 45, 20] } # Creating DataFrame df = pd.DataFrame(data) # Converting DataFrame to a list containing # all the rows of column 'Name' names = df['Name'].tolist() # Printing the converted list. print(names) #['Tony', 'Steve', 'Bruce', 'Peter']value.tolist()
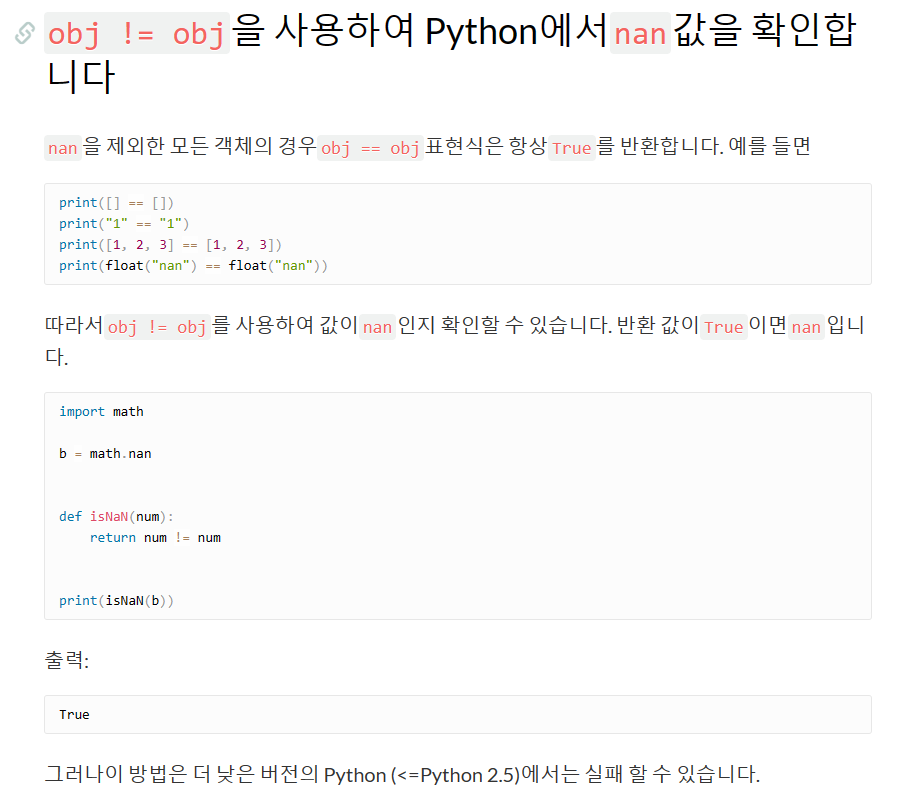
import pandas as pd # Creating a dictionary to store data data = {'Name':['Tony', 'Steve', 'Bruce', 'Peter' ] , 'Age': [35, 70, 45, 20] } # Creating DataFrame df = pd.DataFrame(data) # Converting dataframe to list li = [df.columns.values.tolist()] + df.values.tolist() # Printing list print(li) #[['Name', 'Age'], ['Tony', 35], ['Steve', 70], ['Bruce', 45], ['Peter', 20]]nan 종류
더보기df to list 이후
K = [1,2,3,nan,5] print(type(K[3])) #float이 값을 지정하기 위해서는
for i in K : if pd.isna(i) : 1==1nan_rows = df[df['Credit_History_Age'].isnull()]그 이외에도
np.nan 존재
다른 것도 있을 것 같음
ex) float("nan"), math.nan
+null
이해불가
2차원 배열 차원 하강
더보기sum(list, [ ]) L2 = [x for i in L1 for x in i] #- >? import itertools L2 = list(itertools.chain(*L1)) L2 = list(ltertools.chain.from_iterable(L1)) import numpy as np L2 = np.concatenate(L1).tolist() L2 = np.array(L1).flatten().tolist() from functools import reduce import operator L2 = list(reduce(operator.add, L1))np. ravel(), reshape(), flatten()

in pandas
nunique vs unique
더보기column 1개 내에서 고유값 목록 추출
df['col'].unique() or pd.unique(df['col'])다수 column에서 고유값 목록 추출
pd.unique(df[['col1','col2]].values.ravel())
각 column 내에서 고유값 개수 반환
df['col'].nunique() #(axis =0, dropna = True)다수 column에서 중복 제거 결과 반환 후 갯수 반환
len(df.drop_duplicates()) df.drop_duplicates().shape[0]pd.value_counts()
df.value_counts() #subset=None, normalize=False, sort=True, ascending=False, dropna=Truepd.replace
df.replace() series.replace() #(to_replace=None, value=NoDefault.no_default, inplace=False\ #, limit=None,regex=False, method=NoDefault.no_default)(regex= boolean)
True일 경우 string/pattern을 regular expression pattern으로 인식. False일 경우 string/pattern을 문자 그대로 인식.
to_replace(regex = )
만약 regex=True일 경우 to_replace는 반드시 문자열이여야 한다.
그 대신에 regex의 값이 정규 표현식 또는 정규 표현식의 리스트, 딕셔너리, 배열일 경우 to_replace는 반드시 None(default)이여야 한다.
Regular Expression HOWTO — Python 3.12.3 documentation
Regular Expression HOWTO
Author, A.M. Kuchling < amk@amk.ca>,. Abstract: This document is an introductory tutorial to using regular expressions in Python with the re module. It provides a gentler introduction than the corr...
docs.python.org
최빈값
더보기value_count()
df.value_counts('A').idxmax()[0] df.value_counts('A').max()두 개 이상의 열을 기준으로 가장 많이 등장한 값의 조합을 찾는 경우
(['A', 'B'])
.groupby(' ' )[' ']
df.groupby('A')['A'].count().idxmax() df.groupby('A')['A'].count().max()두 개 이상의 열을 기준으로 최빈 등장 조합 및 횟수
(['A', 'B'])
뒷 부분의 [] 내의 값은 'A', 'B' 둘 다 가능
mode
df['A'].mode()[0] # 가 df.value_counts('A')['가']df_filter
더보기df11 = df10[(df10['Count'] == 2) & (df10['Frequency'] == 2)]filtered_df13 = df[df['Customer_ID'].isin(df13['Customer_ID'])][['Customer_ID', 'Num_Credit_Card']]# Group by 'Customer_ID' and count occurrences of 'Num_Credit_Card' df8 = df.groupby('Customer_ID')['Num_Credit_Card'].value_counts(ascending=False).reset_index(name='Count') # Retain only the 'Customer_ID' and 'Count' columns df9 = df8[['Customer_ID', 'Count']] # Group by 'Customer_ID' again and count the occurrences of each count df10 = df9.groupby('Customer_ID')['Count'].value_counts().reset_index(name='Frequency') # Filter to find cases where the frequency of a certain count is exactly 2 df11 = df10.query("Frequency == 2") print(df11)str.contains(pat, case=True, flags=0, na=None, regex=True)flags : int, default 0 (no flags)
Flags to pass through to the re module, e.g. re.IGNORECASEget_level_values()
?
df행반복
더보기for index, row in df.iterrows(): print(f"{index=}, {row.age=}, {row['sex']=}")for row in df.itertuples(): print(f"{row.age=}, {row.sex=}")for idx in df.index: print(f"{df.loc[idx,'class']=}, {df['age'][idx]=} ({idx=})")for i in range(len(df)): print(f"df.iloc[{i},0] = {df.iloc[i,0]}")다양한 이유 : for문 너무 느리니까 쓰지
groupby, pivot_table 차이점이 궁금합니다 - 인프런 (inflearn.com)
groupby, pivot_table 차이점이 궁금합니다 - 인프런
안녕하세요 선생님, 공부하다가 궁금한게 생겼는데 groupby와 pivot_table 함수의 용도가 거의 똑같은 거 같은데 만약 용도가 다르다면 어느 부분에서 다르고 반약 용도가 비슷하다면 선생님께선 언
www.inflearn.com
'TIL' 카테고리의 다른 글
TIL - 05.21 (0) 2024.05.21 TIL - 05.20 (0) 2024.05.20 TIL - 05.15 (0) 2024.05.15 TIL - 05.14 (0) 2024.05.15 TIL - 05.13 (0) 2024.05.13